Addressing Key Challenges of Lipid-Mediated Delivery Systems for mRNA through Innovation
2020 is anticipated to be an exciting year for the field of messenger RNA (mRNA) therapeutics. Systemic delivery of lipid nanoparticle formulated mRNA (i.e. intravenous, IV dosing) has been a significant challenge for the field of mRNA therapeutics for about 25 years. Arcturus, an emerging leader in the field of lipid formulated mRNA medicines, believes it should be possible to overcome this hurdle by addressing the following two key challenges of lipid mediated delivery systems (LMDSs)–accumulation of lipids in the liver and undesired immune response to the mRNA drug substance.
Lipid Biodegradability
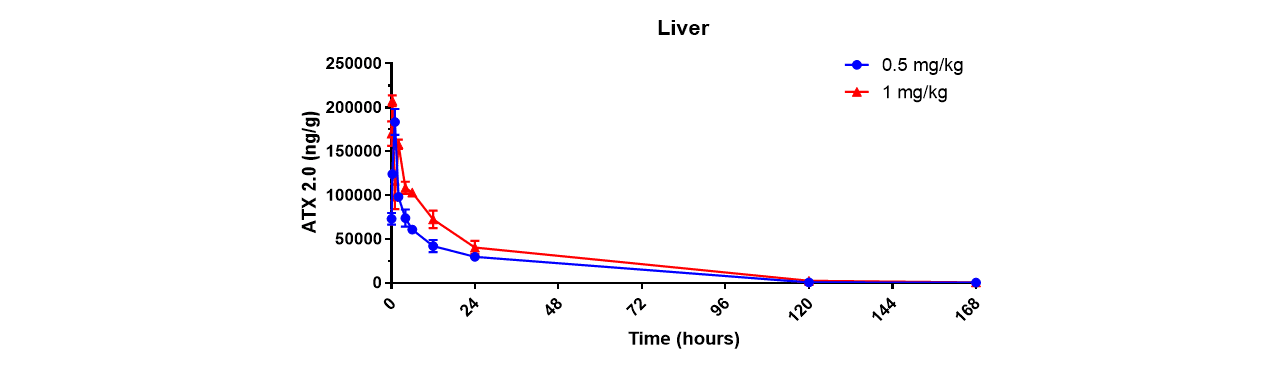
Through an iterative process of rational design and in vivo evaluation, Arcturus has identified various structural motifs that favor fast esterase-catalyzed degradation and has leveraged these learnings to generate a library of proprietary biodegradable lipids, ATX lipids. Arcturus’ LUNAR® technology, a LMDS, is comprised of one or more of these ATX lipids. It is reasonable to expect that the rapid clearance profile observed for ATX 2.0 in the livers of mice (Figure 1) will translate to both non-human primates and patients.
Figure 1: Degradation profile of ATX2.0 in the livers of mice following a single intravenous dose of ATX2.0 formulated mRNA (at mRNA doses of 0.5 and 1.0 mg/kg)
Click on the image to see the full-sized version
Reducing Immunogenicity of mRNA
Producing high purity mRNA is important for any mRNA therapeutic for which activation of the immune response would be undesirable. The Arcturus proprietary mRNA manufacturing process ensures that immunogenic impurities; such as dsRNA, uncapped 5’ mRNA, residual DNA and protein used to produce the mRNA, are kept to a minimum. Arcturus has successfully produced several batches of mRNA (up to the 12-gram scale) to support toxicology and early clinical trials.
Arcturus Prepares for First Clinical Trials with ARCT-810
Utilizing its core platform technologies, Arcturus has been developing a mRNA therapeutic, ARCT-810 (aka, LUNAR®-OTC), for the treatment of ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency (OTCD). OTCD is the most common urea cycle disorder. Because the function of the urea cycle is to metabolize ammonia, a byproduct of protein metabolism, patients with OTCD suffer from elevated ammonia concentrations in the bloodstream (hyperammonemia). Hyperammonemia can result in serious metabolic crisis characterized by vomiting, refusal to eat, progressive lethargy, potentially leading to coma, irreversible neurological damage, or death.
Current Standard of Care
Because OTC is an intracellular protein localized in the mitochondria, treatment of OTCD is not amenable to a traditional enzyme replacement therapy approach. Current front-line therapy involves ammonia scavengers, a low protein diet, hydration, and the use of supplements such as arginine to reduce symptoms. Hemodialysis is sometimes required as an intervention when blood ammonia levels rise too high.
The Promise of a Functional Cure
ARCT-810 is designed to deliver OTC mRNA into liver (hepatocytes) where the urea cycle occurs. Upon release into the cytosol, the cells’ own translational machinery makes the OTC protein and delivers the replacement protein to the mitochondria where it may improve urea cycle activity to reinstate more normal intracellular physiology and potentially correct the disease. Thus, OTC mRNA therapy has the potential to provide a functional cure to patients with OTCD.
Arcturus has recently completed a comprehensive nonclinical program of in vitro and in vivo pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, tissue distribution, and toxicology studies, as well as, cGMP manufacture of drug product and is on track to file an IND in Q1 2020 and subsequently initiate first-in-human clinical trials of ARCT-810.
Arcturus Therapeutics in 2020
2019 saw Arcturus complete a number of financial and collaboration milestones including expansion of the Ultragenyx collaboration for an additional $30M, increased commitment from the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation to $15M, and a successful funding round for $23M with institutional investors. Demonstrating the confidence both of corporate investors and of Pharmaceutical partners in the core LUNAR® technology and leaving the company well-positioned to execute its clinical and preclinical milestones for 2020. In addition to filing IND for its LUNAR-OTC program, Arcturus has two other mRNA therapies in advanced stages of development and pre-clinical evaluation both with key milestones in 2020.
- LUNAR®-GSD3, a partnership program with Ultragenyx working to develop mRNA therapies for Glycogen Storage Disease Type III, which continues to progress towards a 2020+ IND submission. LUNAR®-GSD3 utilizes mRNA therapeutics to replace the defective AGL gene product and allow cells to breakdown glycogen using normal pathways.
- Arcturus is also initiating the development candidate selection process for the LUNAR®-CF Program. An mRNA therapeutic using the LUNAR® delivery platform to deliver Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Receptor (CFTR) mRNA into airway epithelial cells to treat Cystic Fibrosis.
2020 is set up to be a watershed year for Arcturus and the field of mRNA therapy in general, hopefully opening the door to a whole range of new therapies for previously untreated genetic disorders.